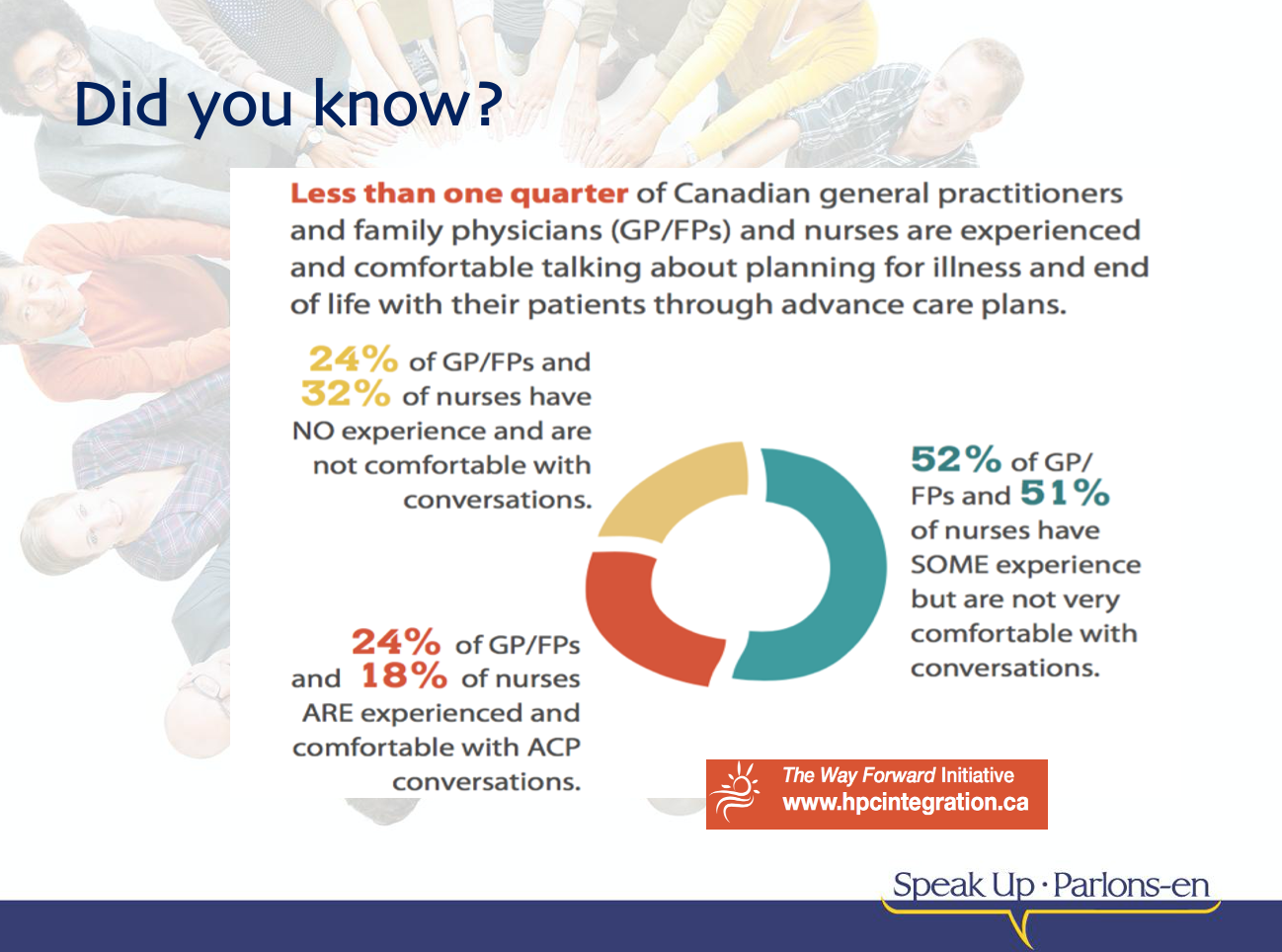
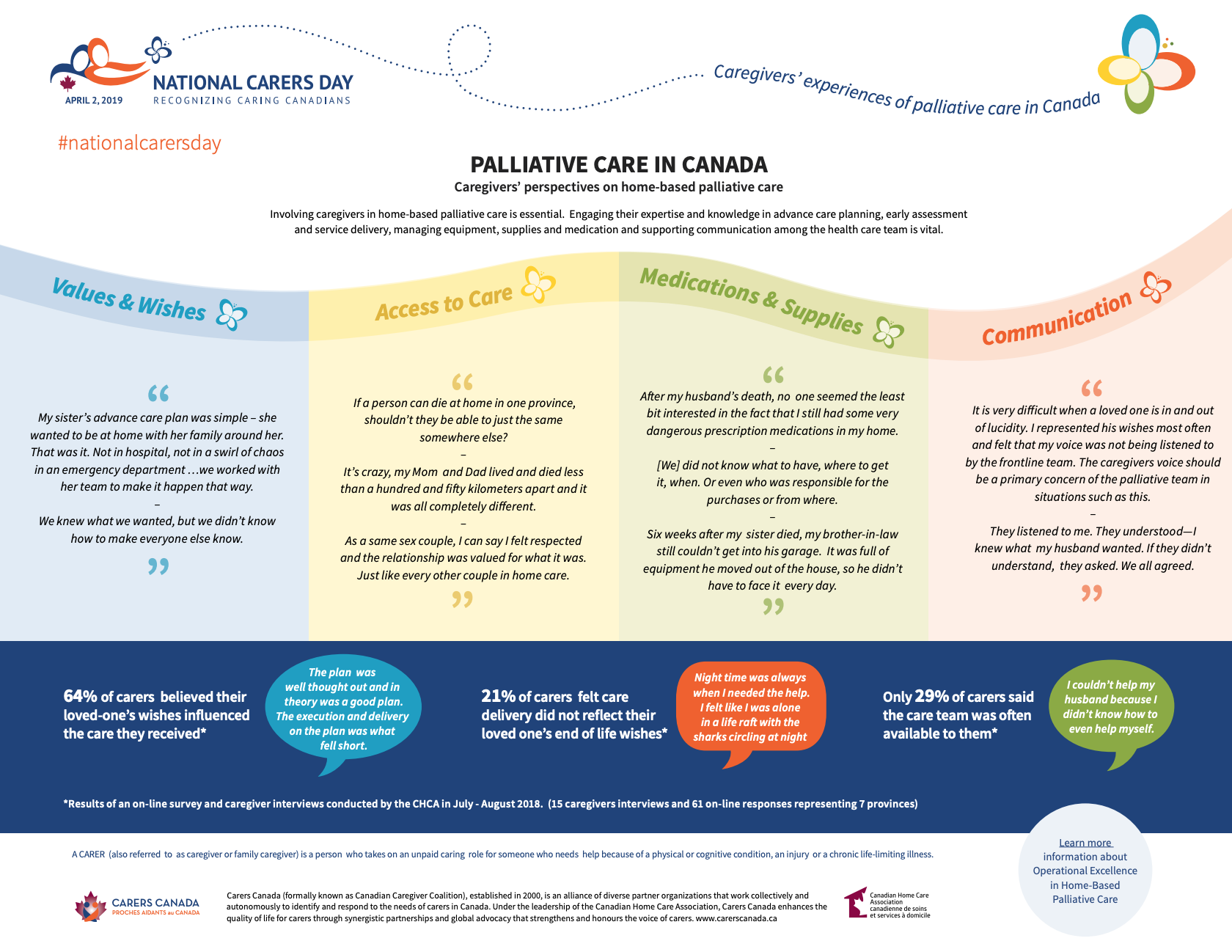
Planning for future healthcare needs is important.
Who would you trust to make healthcare decisions?
Do you know what would happen if you couldn’t communicate for yourself?
Who would you trust to make those healthcare decisions on your behalf?
Think about:
Who you would trust with making important decisions for you.
What matters most in your life and how that might help guide healthcare decisions you would want.
Consider:
Do you know what would happen if you couldn’t decide for yourself?
Who do you trust to make healthcare decisions that respect your wishes?
Would that person (or people) be able to make important decisions about your health in an emergency?
Have you spoken to anyone about what matters most in your life?
What gives you strength in difficult times?
Are spiritual, cultural or religious beliefs, practices, or ceremonies are important to you?
The best time to think about this is NOW (in advance of a medical crisis), while you can make decisions and communicate for yourself. You have the power to choose who that person is. They can be a family member, a friend, or anyone in your life that you trust to make the kinds of healthcare decisions you would want.
Ask yourself: If not you, who?
Source: Advance Care Planning Canada
It is never too early, but it can be too late!
To learn more about Advance Care Planning in 5 Steps, visit Advance Care Planning Canada to access helpful free toolkits and guides to help you along the way.